This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Life Cycle of ACR Carbon Credits
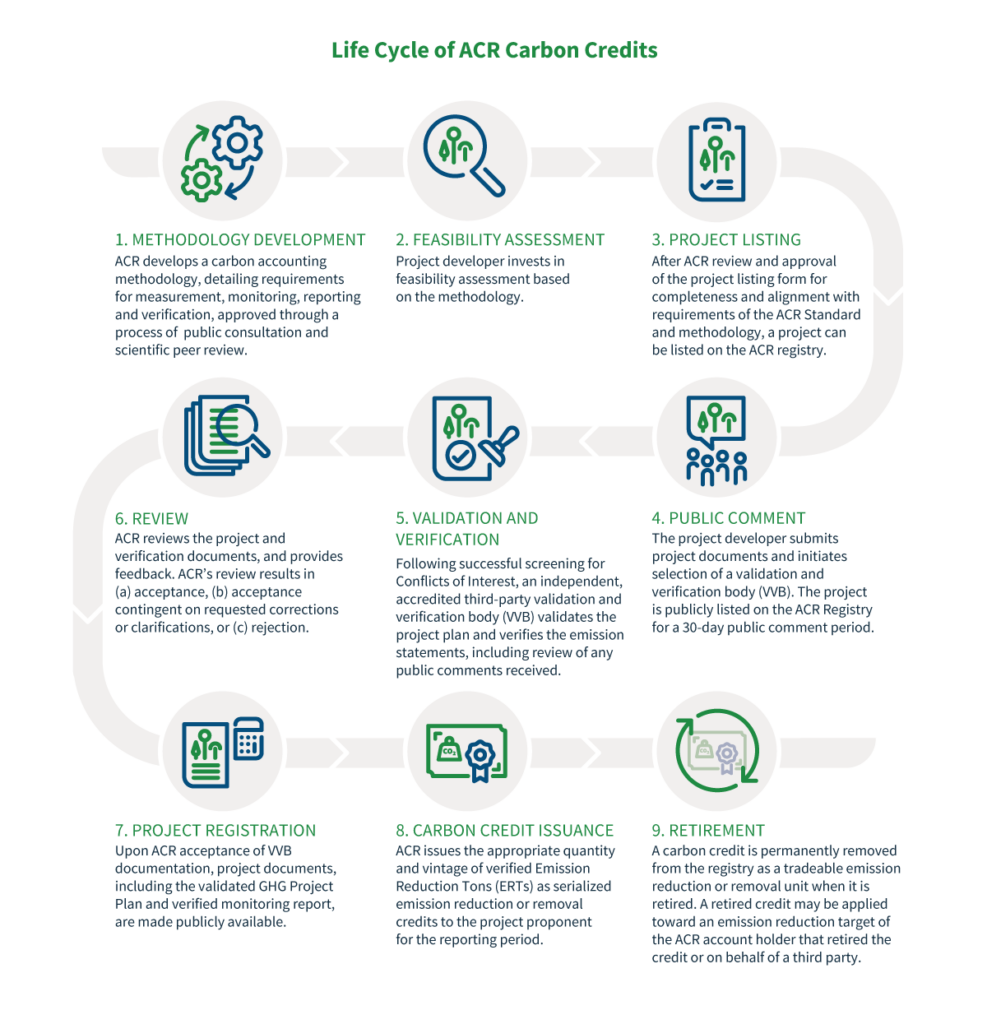
ACR’s process for generating carbon credits using approved methodologies is central to our work. Each step plays an important role in ACR’s ability to create confidence in the integrity of carbon markets to catalyze transformational climate results.
But what is the life cycle of an ACR carbon credit?
The ACR Standard guides the process from start to finish. This ensures that ACR operates a transparent online registry system to record the issuance, transfer, and retirement of serialized carbon credits. ACR oversees the registration and independent verification of greenhouse gas emission reduction and removals projects, and every project submitted for listing must use an active, ACR-approved methodology.
ACR created an infographic to simply and accurately define the steps in the process:
- Methodology development. ACR develops a carbon accounting methodology, detailing requirements for measurement, monitoring, reporting and verification, approved through a process of public consultation and scientific peer review.
- Feasibility assessment. A project developer invests in a feasibility assessment based on the methodology.
- Project listing. After ACR review and approval of the project listing form for completeness and alignment with requirements of the ACR Standard and methodology, a project can be listed on the ACR registry.
- Public comment.The project developer submits project documents and initiates selection of a validation and verification body (VVB). The project is publicly listed on the ACR Registry for a 30-day public comment period.
- Validation and verification. Following successful screening for Conflicts of Interest, an independent, accredited third-party validation and verification body (VVB) validates the project plan and verifies the emission statements, including review of any public comments received.
- Review. ACR reviews the project and verification documents and provides feedback. ACRʼs review results in (a) acceptance, (b) acceptance contingent on requested corrections or clarifications, or (c) rejection.
- Project registration. Upon ACR acceptance of VVB documentation, project documents, including the validated GHG Project Plan and verified monitoring report, are made publicly available.
- Carbon credit issuance. ACR issues the appropriate quantity and vintage of verified Emission Reduction Tons (ERTs) as serialized emission reduction or removal credits to the project proponent for the reporting period.
- Retirement. A carbon credit is permanently removed from the registry as a tradeable emission reduction or removal unit when it is retired. A retired credit may be applied toward an emission reduction target of the ACR account holder that retired the credit or on behalf of a third party.
To promote clarity, consistency, accuracy and impact in the marketplace, we encourage you to use the infographic in your communications.
You can download this infographic about the life cycle of ACR carbon credits here.
